|
A hematoma within the brain parenchyma is known as
intracerebral hematoma. Although it is difficult to define whether it is
contusion or true ICH, it has been reported that they make up at least
30% of all intracranial hematomas.
Etiopathogenesis:
They result from bleeding from damaged vessels deep in the
brain following a trauma.
Acute ICH is mainly of primary type resulting from
arterial bleeding.
When it results from damage to vessels of the brain surface
in the focus of cerebral contusion or laceration, it is called secondary
hematomas.
The majority of both forms occur on the site of cerebral
contusion-in the frontal and temporal regions. Initially they may be
small foci, small fusing bleedings. Hypoxia and acidification of brain
tissues enhance permeability of the vessels resulting in
intracerebral hematomas.
Toxic action of extravasated blood results in brain edema
and raised ICP. ICH may lead to coagulopathy due to release of
thromboplastin from the brain parenchyma.
The traumatic ICHs are most frequently occur in the
temporal, frontal, and parieto-occipital areas.
|
Clinical features:
Decreased level of consciousness, focal signs and symptoms
predominate.
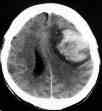
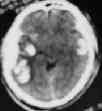
Diagnosis is by CT or MRI scanning.
|
|
|
|
Management:
|
pri.traumatic ICH
|
sec.traumatic ICHs
|
A decisive factor in the management is the clinical picture.
If the GCS is between 3- 9 with no other obvious cause, most
surgeons recommend surgical evacuation and decompression, especially if
the ICH is easily accessible. Stereotactic aspiration is an emerging
technique. Other patients may be treated conservatively and monitored
periodically with serial CTs.
Multiple hemorrhages, especially bilateral, will not benefit
from surgical evacuation.
Aggressive medical management must accompany any surgical
intervention.
The final outcome depends on the preoperative status of the
patient.
|