|
Cysticercosis is probably the most common parasitic
infestation of the human nervous system. Humans acquire the infestation
by eating infected undercooked pork (measly pork). But cysticercosis is
acquired by ingestion of eggs (encysted larvae) of the pork tapeworm,
T.solium, either by ingestion of contaminated salads or water, or by auto
infection due to ano-oral contamination or reverse peristalsis. Tapeworm
infestation can occur only in nonvegetarians, but Cysticercosis may occur
in vegetarians also.
The occurrence of the encysted larvae in the brain, spinal
cord, meninges and eyes is known as neuro-cysticercosis. Cysts may also
occur in the muscles.
A high prevalence has been reported from the developing
countries. The parenchymatous variety is more common in India whereas the
meningeal and ventricular types are more common in South America, Poland
and Mexico.
In India, higher prevalence has been reported in northern
states.
Pathology:
Cysticerci may lodge anywhere in the body, but have a
predilection for the muscle, eye, subcutaneous tissue and CNS. In the
CNS, it can localize in the parenchyma (grey matter), ventricles(4th
ventricle), subarchnoid space and the spinal cord (extramedullary
intradural). In the eye, the vitreous is involved.
A special form, termed cysticercosis reacemosus is a
conglomeration of cysts in the subarchnoid space, is frequently seen in
Latin America.
Once the larva dies, it calcifies. The cysts vary in size
and often multiple. The inflammatory response is variable. At times it
may contain scolices.
Pathologically, it may result in meningo-encephalitis,
granulomatous meningitis, focal granulomas or abscess, hydrocephalus,
ependymitis and arteritis.
Clinical features:
They may present with one or more of various syndromes
namely, seizures, raised ICT, ICSOL like, meningoencephalitis,
psychiatric disorders and stroke, and radiculopathy or myelopathy, if the
spinal cord is involved.
Epilepsy is the commonest manifestation in India.
Increased ICT is the next commonest, simulating benign ICT.
Meningoencephalitis presents with a pyrexia, altered
sensorium, seizures, raised ICT, multiple cranial nerve involvement and
brainstem and cerebellar involvement have been reported.
Ischaemic effects seem to affect the young.
Subcutaneous nodules and ocular cysts are important
indicators.
Diagnosis:
There is eosinophilia in the blood and CSF. Biopsy of the
subcutaneous nodules, if any, may help.
Serological tests are nondiagnostic on their own. These
include, indirect haem-agglutination test and enzyme linked immunosorbent
assay (ELISA) which is about 80% sensitive in CSF. False positives may
occur in patients with hydatid, filariasis, TBMs and viral encephalitis.
Those with active inflammatory response are likely to have high titers,
as expected. Those with intraventricular cysts have a low titer.
Lately, the enzyme linked immuno electro transfer blot
(EITB) test has been introduced and reported to be 100% sensitive in
patients with two or more viable lesions.
|
Radiological appearances:
The ventricles may be narrowed with extensive low
attenuated areas in the parenchyma, sparing the cortex.
A ring enhancing active lesion with surrounding edema is
the second common.
A homogeneously enhancing lesion represents a dying larva.
Calcified lesions are also common in CT.
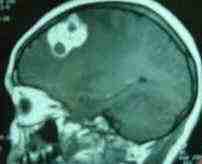
The racemose type appears as a bunch of grapes.
The intraventricular types are better seen in MRI.
MRI may reveal scolex as an high intensity inside a cyst.
Treatment:
Praziquantel and albendazole are available. Opinions
differ on dosage and duration and the need for a second course.
Some recommend combined therapy.
Praziquantel:
50 mg/kg for 15 days. A second course is usually not
of any benefit.
Side effects include headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting,
parasthesias and skin erythema.
Albendazole : more effective.
|
|
|
|
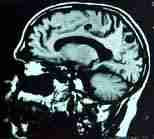
MRI-hypodense cysts
|
|
|
|
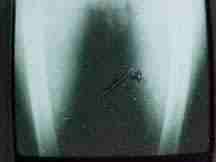
Calcified cysts
in the thigh
|
|
|
|
Racemose
Cysticercosis-MRI
|
|
15mg/kg in thrice daily for one month is the usual practice.
Recent reports suggest even a three days course is as effective.
Side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms, alopecia,
rash and pruritis.
Contraindicated in pregnancy and children of less than two
years.
Major side effects of these drugs are deterioration in
neurological status, exacerbation of seizures and rise in ICP due to host
reactions to the dying parasites, more so with praziquantel. A short
course of steroids help.
Intraventricular cysts require surgery-excision / or a
shunt.
Racemose variety does not respond to drug therapy and need
excision.
Decompressive craniotomy may be life/vision saving on
occasions.
Spinal variety usually undergo surgery to confirm the diagnosis
and releive the cord
Serological tests are nondiagnostic on their own. These
include, indirect hemagglutination test and enzyme linked immunosorbent
assay (ELISA) which is about 80% sensitive in CSF. False positives may
occur in patients with hydatid, filariasis, TBMs and viral encephalitis.
Those with active inflammatory response are likely to have high titers,
as expected. Those with intraventricular cysts have a low titer.
|