|
MANAGEMENT:
Papilledema
could be VISION THREATENING.
Though
there are exceptions, the public and all doctors are well aware about
the importance of an eye examination in a case of headache when related
to visual work or when associated with visual disturbances like
diplopia and vomiting.
When
often patients visit ophthalmologists for headache, we rule out other
causes of headache like refractive errors, ocular muscle imbalance,
ocular inflammation and glaucoma in them .Later we specifically look at
the optic disc for obtaining an insight to the cause of headache.
When
it is a case of disc edema it is extremely important to know whether
it is true disc edema or pseudopapilledema and whether we are
dealing with a case of optic neuritis .
A
careful history like hypertension, diabetes etc., taking into account
the various causes should be elicited. It should also include drug
history particularly overdosage of Vitamin A, oral
contraceptives, anti psychotics and others.
A
complete and thorough eye check up comprising of visual acuity, visual
fields, refraction (with appropriate cycloplegic especially in
children, and slit lamp examination of the fundus, vitreous, and
macula.
We
should also have an idea of the stage of papilledema.
Investigations:
Floresin
angiography
(FFA) will show leak in cases of disc edema. This test should be
carried out only when doubtful as it only helps in differentiating true
from pseudo papilledema but not optic neuritis from papilledema.
When
ophthalmic cause is ruled out, an opinion by neurologist or
neurosurgeon should be sought to establish the diagnosis.
MRI of the brain
with or without contrast should be carried out.
Guarded
LP for C.S.F analysis or for reduction of ICT during dire
emergency with manometry.
Treatment:
If
papilledema is due to intracranial cause then anti-edema measures and
the underlying causes have to be detected and treated ( ATT for
tuberculoma, withdrawal of oral contraceptives, withdrawal of
antipsychotics, removal of intracranial SOL or shunting of
associated hydrocephalus etc).
In
benign ICT-Acetazolamide is the drug of choice especially the
sustained release variety due to lesser side effects because of BD,OD
or AD dosage.Regular variety has to be consumed 4 times a day and side
effects like paraesthesia are more and reduces the compliance.Liver
function tests and hemogram have to be done periodically. Most of the
cases spontaneously resolve but some of them may continue to have
headache and visual loss. When visual deterioration is detected despite
adequate antiedema measures, a lumbo-Peritoneal or subtemporal
decompression is done by the neurosurgeon.
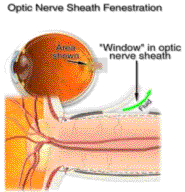
Lately,
Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration is preferred and carried out by
a team of E.N.T, Neuro and eye surgeons.
Transnasal
endoscopic approach would be preferable these days because both optic
nerve sheaths can be tackled in the same sitting, and the Optic
canal can be directly approached and optic nerve sheath visualized. The
risks are infection and transfer of heat while working with burr in the
vicinity of optic nerve. Continuous irrigation with water will be of
help. Appropriate and adequate coverage with antibiotics will reduce
chances of infection.
Role
of ophthalmologist in management during the course of papilloedema:
Combined
team work and clear communication and cooperation amongst the treating
doctors will do wonders for the patient. A multidisciplinary approach
in fact, is mandatory.
Ophthalmologist
should guide the neurophysician and neurosurgeons by carefully
monitoring the visual acuity and color vision by Ishihara chart.
However when patient has difficulty in perceiving colors like before,
he / she is asked to report promptly.
Visual
fields monitoring–The appearance of overall peripheral constriction in
serial autoperimetry provides more valuable information rather than the
fundus picture for florid stage going into chronic and atrophic. Visual
acuity decreases after that. It is not advisable to wait until then. It
could denote the ?commencement of irreversible damage of the axons in
the optic nerve –This should ring an alarm and the
ophthalmologist should warn the neuro faculty about the urgency
of the situation to step up the antiedema measures or intervene
surgically at the earliest.
The
author would like to share some of the experiences with illustrating
cases.
Case
– 1 :
A
fourteen year old female with complaints of headache for one year had
consulted several doctors. A diagnosis of depression was made. Having
got no relief she finally came down to Chennai. The neuro surgeon
subjected her to investigations.
MRI
showed SOL. Stereotactic biopsy and HPE confirmed it as a case of
tuberculoma.
|
Neuro
ophthalmic examination showed –Right eye BCVA 6/18, 16/16 color
vision ,disc edema and hyperemia with peripapillary sheathing and
macular exudates and normal visual fields. In the left eye the vision
was hand movements, and mild pallor of the disc.
The
clinical picture remained status quo with ATT and anti-edema
measures. Ethambutol was deliberately avoided for its neuro toxicity
on the optic nerves.
After
that the right eye began to show peripheral constriction despite IV
mannitol etc. Only few days later the VA dropped from 6/18 to HM in
RE and no PL in LE (picture B).
Repeat
MRI showed decrease of perilesional edema .
Following
discussions, a decision to perform trans nasal endoscopic
decompression bilaterally in the same sitting under GA was made and
carried out after explaining the risk of loosing vision and
possibility of developing infection. At the end of the surgery CSF
was let out.
|
|
|
|
Schematic picture
|
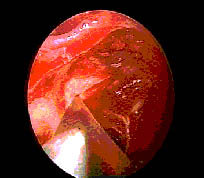
Peroperative
picture-the optic nerve sheath being fenestrated.
|
Though
vision improved transiently to CFCF for 2 days she was PL –VE for 2
months. She then regained vision in Right eye to 6/6, visual fields
full and could pursue her normal life and studies.
Please
Note:
ONSF
can be also be done transconjunctivally by the ophthalmologist on one
side at a time. Surgery on one optic nerve can reduce the pressure on
contralateral optic nerve .But T / N endoscopy was adopted because as
mentioned earlier it gives best access to the optic canal with least
injury to the optic nerve. While tackling the outer part of canal
bone with burr, the heat generated can be lessened by continued
irrigation. The inner part should be curetted.
Mitomycin
- C application on the optic nerve sheath before the
fenestration has found to maintain the patency of the fistula.
ONSF
is nowadays being recommended for secondary causes of
increased ICT too.
|
|
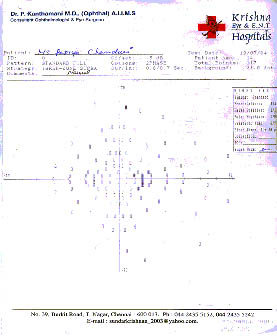
(A) visual fields of RE
|
|
|
|
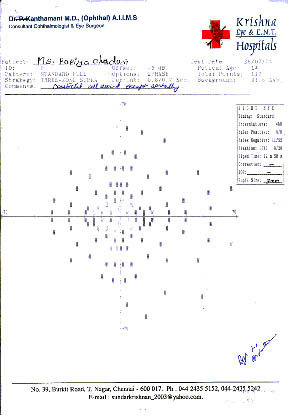
(B)visual fields of LE
|
|
|
|
Case
- 2:
A
15 yr old female had headache for 1 yr .Ophthalmic examination was done
elsewhere only at the beginning. Since it was found to be normal she
used to take analgesics for relief. Finally when she developed vomiting
and swaying gait, choroidal plexus tumor in the CPA was diagnosed
.Despite surgical, radiotherapy and antiedema measures, her papilledema
rapidly progressed and VA deteriorated drastically in a week’s
time .She is now with only CFCF angular in RE and no PL in LE.
A
word of caution!
If
the SOL is a choroidal plexus tumor, the rate of progression of
papilledema is alarmingly rapid and accelerated so much so that the
patient goes from florid to chronic and atrophic in no time and looses
vision unless timely and appropriate management are rendered.
During
radiotherapy for various intracranial space occupying lesions, ICT can
raise due to cerebral edema. Concomitant anti edema measures will
reduce the burden on the optic nerves.
Case
-3:
A
30 yr old female was referred as a case of papilledema by neuro surgeon
for neuroophthalmic examination. Slit lamp examination showed mild bilateral
anterior uveitis. Sarcoidosis was suspected and confirmed. The disc
edema and uveitis responded to oral prednisolone. Topical steroids and
cycloplegic drops were also given. It was a case of B / L disc
edema due to sarcoidosis.
Case-4:
A
55 yr old male was referred to as a case of papilledema for
neuroophthalmic examination. He was being investigated for brain
metastasis at a tertiary care hospital. His BP was recorded normal all
through out by staff nurse. He was previously treated for malignancy in
the neck successfully. But fundus examination showed arterial
attenuation in addition to disc edema. The BP was personally recorded
and found to be 220/160 mm Hg. MRI and CSF analysis were normal. It was
a case of grade - 4 HYPERTENSIVE RETINOPATHY.
Case-5:
A
40 yr old female was referred for headache to us by medical
oncologist. She was a known case of Recurrent B Cell Lymphoma of the
lungs. O / E she was found to have neovascular glaucoma in LE . Fundus
examination revealed partial block of both central retinal
arteries and optic discs had blurred margins. Media was hazy in Left
Eye. There was both central retinal artery and vein occlusion in the
Right Eye. A diagnosis of infiltrative optic neuropathy was made. MRI
of brain showed optic nerve thickening correspondingly. Radiotherapy
helped in resolution of edema and improvement of vision.
Case-6:
A
10 yr old girl complained of severe headache and vomiting for few days
. Her ophthalmic examination showed papilloedema in both eyes. Careful
history revealed that the child was taking Vitamin A 50000 IU everyday
for the preceding 3 months though she was advised the treatment only
for few days. Discontinuation of Vit A reversed papilledema and
relieved the symptoms. Similarly 40 yr old female from Calcutta, a
teacher by profession was found to have papilledema and benign ICT. The
antidepressant she was taking was the causative factor. She was alright
in few days after she stopped taking the medicine.
|