|
Echinococcosis:
Echinococcus granulsus(dog tapeworm) produces hydatid
disease in man and in other animals and is endemic in sheep rearing
areas. Itís larval form is called the hydatid cyst. Ingestion of
contaminated food infected with the ova infects man. The eggs release
embryos in the stomach. The embryo passes through the liver and
systemic circulation to the CNS, the cranium and vertebrae.1% of all
ICSOLs in New Zealand were hydatid cysts. In India it is about 0.2%.
Pathology:
It is an unilocular cyst containing watery, colorless
fluid.The wall has an outer thin layer, intermediate layer of
laminated chitinous material and an inner germinal layer to which are
attached brood capsules, containing scolices.The cyst is almost
always confined to the white matter and supratentorial.There is no
neural tissue reaction and causes raised ICT by its size and
interference with CSF pathways.
Hydatid disease of the cranium is a primary disease. It
involves the diploe.As it grows there is localized thinning of the
skull in both directions and eventual erosion and presents
extradurally. The dura is rarely involved.
Involvement of the spinal cord is rare and a vertebral
involvement should be ruled out which is also rare. Usually the
pedicle is involved.
Clinical features:
In adults focal neuro signs predominate.
In children the features of raised ICT predominate.
Cranial cysts present as a lump beneath the scalp.
Vertebral involvement present as a para vertebral lump
and later with myelopathy. The thoracic spines are commonly affected.
|
|
|
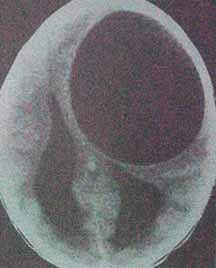
CT
showing the hydatid cyst
|
Diagnosis:
A raised eosinophil count and a positive Casoni's
intradermal test may help. When there is suspicion, indirect
haemagglutination, immunoelectrophoresis and indirect
immunofluorescence should be carried out.
Radiological appearances:
The skull vault may show thinning, erosion and bulging.
The CT reveals an intrapararenchymal hypodense lesion
with well-defined margins and no perilesional edema. Contrast enhancement
suggests secondary infection.
Treatment:
Surgical excision is the treatment with out rupturing
the cyst. A large craniotomy and radiating cortical incisions
followed by irrigation of the cleavage between the cyst and brain
delivers the intact cyst.
In case of accidental spillage, generous irrigation is
advised.
Praziquantel may be used in case of spillage. Some
recommend albendazole along with praziquantel.
Amoebiosis:
Entamoeba histolytica has a worldwide distribution, more
so in tropics. Organisms reach the CNS by embolization from a liver
or lung primary. They cause necrosis, edema, seizures and
occasionally an abscess.
Preoperative diagnosis is impossible. It may be
suspected in patients with liver/ lung lesions.
Treatment is by aspiration and drainage. Emetine
injections along with chloroquine (500mg a day) along with
metronidazole 500mg 6 hrly are useful. Secondary infections may
require a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Cerebral Malaria:
Plasmodium falciparum is responsible. They cause
agglutination of the infected RBCs leading to extensive occlusion of
the brain capillaries. The lesions are more prominent in the grey
matter. Perivascular hemorrhages are common.
Intravenous quinine sulphate and vigorous measures to
bring down the hyperpyrexia may help.
Toxoplasmosis:
Toxoplasma gondi is an intracellular parasite found in
reticuloepithelial cells. The disease, when congenital, is through
the placenta. The infection may also be transmitted through mother's
milk. In older children and adults the infection is by ingestion of
infected meat, milk or eggs.
There is special predilection for the developing foetus
nervous system. Any child with mental retardation and convulsions
should be investigated for toxoplasmosis.
In adults, it is the most common opportunistic infection
of the CNS. In patients with AIDS it is a very common cause of
ICSOL.
|
CT may reveal multiple ring lesions.
Studies suggest a relationship of toxoplasma to
gliomas.
Treatment is not satisfactory.
Pyremethamine and sulfadiazine help.
Trichinosis:
This roundworm occasionally precipitates encephalitis.
Granulomatous nodules and small vessel vasculitis develop in the
brain. Usual mode of infection is by eating infected pork.
Thiabendazole and steroids help.
|
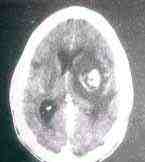
CT
showing toxoplasmosis
|
|